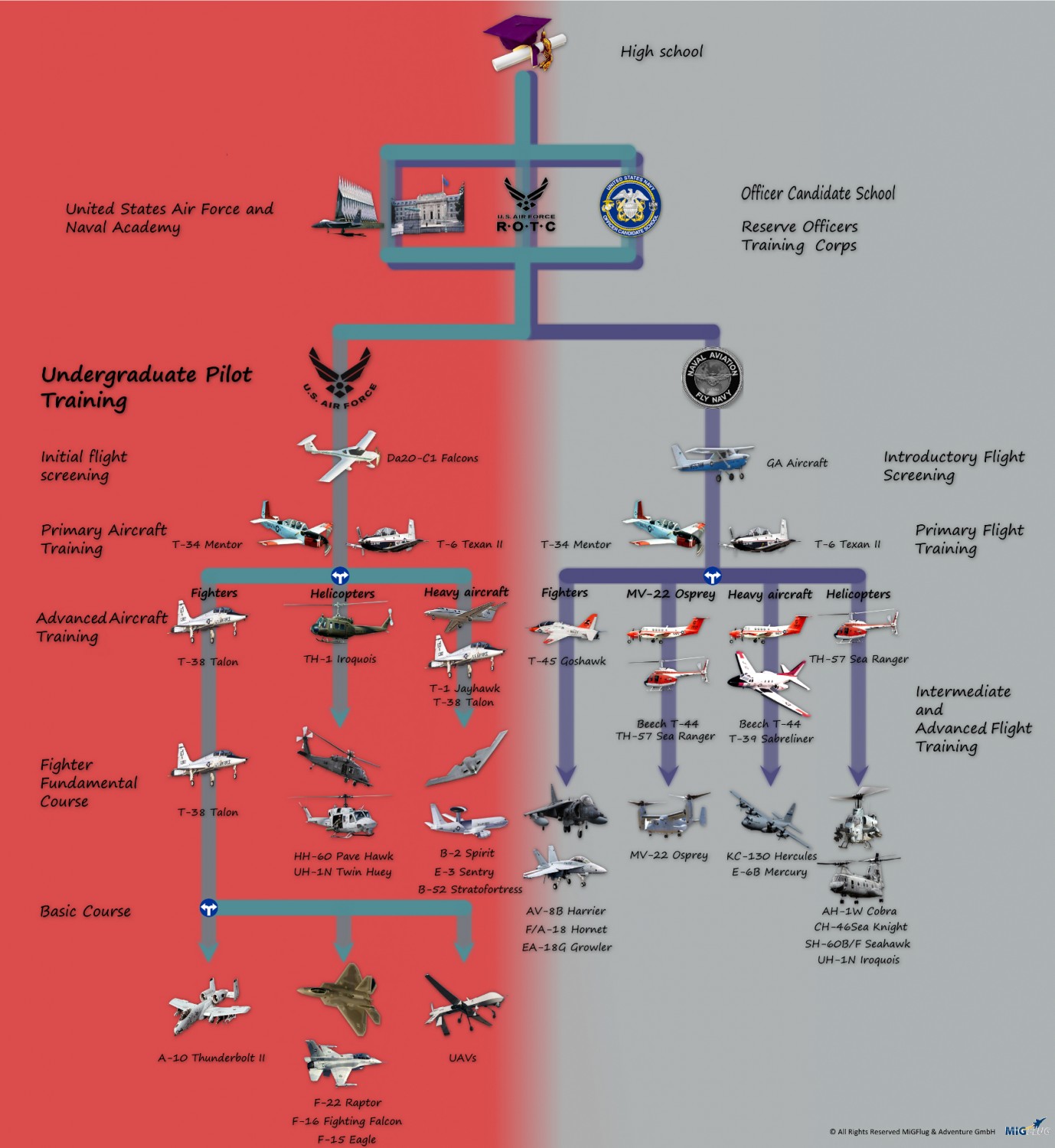
Flying an aircraft is a dream for many, but the path to becoming a pilot requires dedication, education, and skill development. Understanding the steps to becoming a pilot can help aspiring aviators navigate this rewarding profession. Whether you wish to fly commercially, privately, or as part of the military, each path offers unique challenges and rewards. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview that will prepare you for the journey ahead.
Becoming a pilot involves more than just learning to fly an aircraft. It encompasses understanding aviation regulations, acquiring technical skills, and developing the ability to make quick decisions under pressure. With the right education and training, you can transform your passion for aviation into a successful career. This guide will walk you through the essential steps, from selecting a flight school to obtaining a pilot's license, and everything in between.
To achieve your dream of flying, it's crucial to understand the variety of pilot licenses available, the requirements for each, and the potential career paths you can pursue. With dedication and determination, you can join the ranks of those who call the skies their office. Let's explore what it takes to make your dream of becoming a pilot a reality.
Read also:Discovering The Vibrant Lifestyle And Opportunities In Kootenai County
Table of Contents
- What is a Pilot?
- Types of Pilot Licenses
- Why Choose a Career as a Pilot?
- Educational Requirements
- How to Choose the Right Flight School?
- Understanding Flight Training Programs
- What are the Medical Requirements?
- Gaining Flight Experience
- How to Pass the Pilot Licensing Exam?
- Career Paths for Pilots
- Continuing Education for Pilots
- What are the Challenges of Being a Pilot?
- Important Regulations and Safety Protocols
- How to Maintain a Balanced Lifestyle as a Pilot?
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Pilot?
A pilot is a skilled individual who is trained to operate aircraft and navigate the skies. They are responsible for ensuring the safety of their passengers, crew, and cargo while adhering to aviation regulations and protocols. Pilots play a crucial role in the aviation industry, facilitating global connectivity and contributing to the economy by transporting goods and people efficiently.
Pilots can work in various sectors, including commercial, military, private, and cargo aviation. Each sector requires specific skills and knowledge, with commercial and military pilots often undergoing more rigorous training and certification processes. Regardless of the sector, pilots must possess excellent communication, problem-solving, and decision-making skills to handle the dynamic nature of aviation.
Becoming a pilot involves a combination of education, training, and practical experience. Aspiring pilots must obtain the necessary licenses and certifications, which vary depending on the type of aircraft they wish to operate and the specific career path they choose. This journey requires dedication and a deep passion for aviation, as pilots must continually update their skills and knowledge to stay current with industry standards and advancements.
Types of Pilot Licenses
Understanding the different types of pilot licenses is essential for choosing the right path in your aviation career. Each license serves a specific purpose and comes with its own set of requirements and privileges. Here are the main types of pilot licenses:
1. Student Pilot License (SPL)
The Student Pilot License is the first step for anyone aspiring to become a pilot. It allows you to start your flight training under the supervision of a certified flight instructor. With an SPL, you cannot fly solo or carry passengers, but it provides the foundational skills needed for further training.
2. Private Pilot License (PPL)
A Private Pilot License grants you the freedom to fly as the pilot-in-command of an aircraft for personal or recreational purposes. With a PPL, you can carry passengers but cannot be compensated for flying services. This license requires a minimum number of flight hours, a successful medical examination, and passing a written and practical exam.
Read also:Delve Into The Charms Of The Pennsylvania Big Apple
3. Commercial Pilot License (CPL)
The Commercial Pilot License allows you to be paid for your flying services. It's a crucial step for those who want to pursue a career in aviation. To obtain a CPL, you must have a higher number of flight hours compared to a PPL and pass additional tests related to aerodynamics, navigation, and regulations.
4. Airline Transport Pilot License (ATPL)
An Airline Transport Pilot License is the highest level of pilot certification and is required to act as the pilot-in-command of an airline aircraft. It demands extensive flight experience, passing rigorous exams, and meeting strict medical requirements. The ATPL is a prerequisite for captaining commercial airliners.
5. Recreational Pilot License (RPL)
The Recreational Pilot License is designed for those who wish to fly for fun and leisure. It has fewer requirements than a PPL, making it an attractive option for hobbyists. However, it has limitations on the type of aircraft you can fly, the distance you can travel, and the conditions in which you can operate.
6. Sport Pilot License (SPL)
The Sport Pilot License is intended for those interested in flying light-sport aircraft. It has fewer training hours required compared to other licenses, making it a quicker and more cost-effective option for recreational pilots. However, it also comes with restrictions on aircraft type, passenger carrying, and flight conditions.
Choosing the right license depends on your career goals, interests, and the type of flying you wish to pursue. Each license serves as a stepping stone to more advanced certifications and opportunities within the aviation industry.
Why Choose a Career as a Pilot?
Choosing a career as a pilot offers numerous benefits and opportunities that make it an attractive profession for many aviation enthusiasts. Here are some compelling reasons to consider becoming a pilot:
- Passion for Flying: For many, the love of flying is the primary motivation for becoming a pilot. The thrill of taking off, navigating through the skies, and landing safely is a source of immense satisfaction.
- Travel Opportunities: Pilots have the unique advantage of traveling to various destinations as part of their job, experiencing different cultures, and visiting places they might not otherwise see.
- Exciting and Dynamic Work Environment: The aviation industry is constantly evolving, offering pilots a dynamic and challenging work environment. Every flight brings new experiences and opportunities to learn.
- Career Advancement: The aviation industry offers numerous career advancement opportunities. Starting as a co-pilot, you can progress to a captain's position, take on management roles, or even transition to aviation training or safety positions.
- Job Stability and Demand: The demand for pilots is on the rise globally, with airlines expanding their fleets and routes. This demand ensures job stability and competitive salaries for qualified pilots.
- Personal Development: Being a pilot requires constant learning and skill development. This continuous growth contributes to personal development and enhances critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making skills.
A career as a pilot is not without its challenges, but the rewards and opportunities make it a fulfilling and exciting profession. For those with a passion for aviation and a desire to make a difference in the world of flight, becoming a pilot is an excellent choice.
Educational Requirements
Becoming a pilot requires a combination of formal education, specialized training, and practical experience. Here are the key educational requirements you need to fulfill:
1. High School Diploma or Equivalent
The first step to becoming a pilot is obtaining a high school diploma or its equivalent. High school courses in mathematics, physics, and geography can provide a solid foundation for understanding aviation principles.
2. College Degree (Optional)
While not mandatory, a college degree can enhance your career prospects and provide additional knowledge useful in aviation. Degrees in aviation, engineering, or related fields are particularly beneficial.
3. Ground School Training
Ground school training is an essential part of pilot education, covering topics such as aerodynamics, navigation, meteorology, and aviation regulations. This theoretical knowledge prepares you for the practical aspects of flying.
4. Flight School Training
Flight school training is where you gain hands-on flying experience. Under the guidance of certified flight instructors, you'll learn to operate aircraft, perform maneuvers, and handle emergencies. This training is crucial for obtaining your pilot license.
5. Flight Hours
Accumulating flight hours is a critical requirement for obtaining a pilot license. The number of hours varies depending on the license type you pursue, with a minimum requirement for each. Gaining diverse flying experience in different weather conditions and aircraft types is beneficial.
6. Licensing Exams
You must pass written, oral, and practical exams to obtain your pilot license. These exams test your theoretical knowledge and practical flying skills, ensuring you're well-prepared to operate an aircraft safely.
Meeting these educational requirements is essential for becoming a competent and qualified pilot. With dedication and commitment, you can navigate the educational path and achieve your dream of flying.
How to Choose the Right Flight School?
Selecting the right flight school is a crucial step in your journey to becoming a pilot. The quality of your training significantly impacts your skills and career prospects. Here are some factors to consider when choosing a flight school:
1. Accreditation and Certification
Ensure the flight school is accredited by relevant aviation authorities and offers certified training programs. This accreditation guarantees the school meets industry standards and provides quality education.
2. Reputation and Reviews
Research the school's reputation in the aviation industry. Read reviews and testimonials from former students to gauge their experiences and satisfaction with the training they received.
3. Training Programs Offered
Check the range of training programs the school offers, including the types of licenses and ratings you can obtain. Make sure the school aligns with your career goals and provides the training you need.
4. Instructor Experience
The experience and qualifications of flight instructors are crucial for effective learning. Look for schools with experienced instructors who have a solid track record in training successful pilots.
5. Fleet and Facilities
Evaluate the school's fleet of aircraft and facilities. A diverse fleet with modern equipment provides a better learning experience, while well-maintained facilities contribute to a conducive training environment.
6. Cost and Financial Aid
Consider the cost of training and the availability of financial aid or scholarships. Flight training can be expensive, so understanding the financial commitment and exploring funding options is essential.
Choosing the right flight school is a pivotal decision in your pilot training journey. By considering these factors, you can make an informed choice that sets you on the path to success in your aviation career.
Understanding Flight Training Programs
Flight training programs are designed to equip aspiring pilots with the necessary skills and knowledge to operate aircraft safely and efficiently. Understanding these programs is crucial for selecting the right training path. Here's an overview of key components:
1. Private Pilot Training
Private pilot training is the entry-level program for aspiring pilots. It covers fundamental flying skills, aircraft operation, navigation, and communication. The program includes ground school instruction and practical flight training, culminating in a private pilot license.
2. Instrument Rating
An instrument rating allows pilots to fly under instrument flight rules (IFR), enabling them to navigate through poor weather conditions using cockpit instruments. This training focuses on advanced navigation techniques and enhances pilot proficiency and safety.
3. Commercial Pilot Training
Commercial pilot training prepares pilots for a professional career in aviation. It includes advanced flight maneuvers, emergency procedures, and multi-engine aircraft operation. This training is essential for obtaining a commercial pilot license, allowing pilots to be compensated for their services.
4. Multi-Engine Rating
A multi-engine rating provides the skills needed to operate aircraft with more than one engine. This training is crucial for pilots aiming to fly larger, more complex aircraft in commercial aviation.
5. Airline Transport Pilot Training
Airline transport pilot training is the pinnacle of flight training, designed for those seeking to become airline captains. It covers advanced flight techniques, leadership skills, and crew resource management. This training is a prerequisite for obtaining an airline transport pilot license.
6. Flight Instructor Training
Flight instructor training prepares pilots to teach others how to fly. It involves learning instructional techniques, curriculum development, and student assessment. Becoming a flight instructor is an excellent way to gain experience and hours while sharing your passion for aviation.
Flight training programs vary in duration, cost, and intensity, depending on the license or rating pursued. Understanding these programs enables aspiring pilots to choose the right path and achieve their aviation goals.
What are the Medical Requirements?
Meeting medical requirements is a critical aspect of becoming a pilot. Pilots must maintain a certain level of physical and mental fitness to ensure the safety of themselves, their passengers, and their aircraft. Here are the key medical requirements for pilots:
1. Medical Certification Classes
There are three classes of medical certification for pilots, each with specific requirements:
- Class 1: Required for commercial airline pilots, this certification has the most stringent medical standards.
- Class 2: Required for commercial pilots who do not fly passengers, such as crop dusters or flight instructors.
- Class 3: Required for private pilots and has the least stringent medical requirements.
2. Vision and Hearing
Pilots must have good vision and hearing. Corrective lenses are allowed if they achieve the required standard. Vision tests assess distance and near vision, color vision, and peripheral vision.
3. Physical Health
Pilots must be in good physical health, free from conditions that could impair their ability to fly safely. Medical examinations assess cardiovascular health, respiratory function, and other vital systems.
4. Mental Health
Mental health is equally important for pilots. Conditions such as severe anxiety, depression, or other psychiatric disorders may disqualify an individual from flying. Regular assessments ensure pilots maintain mental fitness.
5. Substance Use
Pilots must have a clean record regarding substance use. Regular drug and alcohol testing is conducted to ensure pilots are not under the influence while operating an aircraft.
Obtaining and maintaining medical certification is essential for a pilot's career. Regular medical examinations ensure pilots remain fit and capable of performing their duties safely. Understanding these requirements helps aspiring pilots prepare for and meet the necessary health standards.
Gaining Flight Experience
Acquiring flight experience is a crucial step in the journey to becoming a pilot. It not only fulfills the requirements for obtaining various pilot licenses but also builds confidence and proficiency in operating aircraft. Here's how aspiring pilots can gain valuable flight experience:
1. Flight School Training
Flight school provides structured training and supervised flight hours. Under the guidance of certified instructors, students practice takeoffs, landings, navigation, and emergency procedures, gaining hands-on experience in a controlled environment.
2. Solo Flights
Solo flights are a significant milestone in a pilot's training. They offer the opportunity to fly without an instructor, building confidence and independence. These flights are conducted once the student demonstrates proficiency in basic flying skills.
3. Cross-Country Flights
Cross-country flights are essential for gaining navigation experience and understanding air traffic control procedures in different regions. These flights require planning, coordination, and problem-solving, enhancing a pilot's overall skill set.
4. Night Flying
Night flying experience is crucial for pilots seeking advanced licenses. It involves flying in reduced visibility conditions, requiring pilots to rely on cockpit instruments and develop spatial awareness. Night flights are often part of commercial pilot training.
5. Diverse Weather Conditions
Flying in various weather conditions helps pilots develop adaptability and decision-making skills. Experience in handling turbulence, wind, rain, and other weather phenomena is invaluable for ensuring safe flights in real-world scenarios.
6. Additional Ratings
Obtaining additional ratings, such as instrument or multi-engine ratings, provides specialized experience and enhances a pilot's qualifications. These ratings involve advanced training in specific areas, broadening a pilot's capabilities.
Gaining flight experience is an ongoing process that continues throughout a pilot's career. Each flight offers new learning opportunities, contributing to skill development and confidence building. By actively seeking diverse flying experiences, aspiring pilots can accelerate their progress and achieve their aviation goals.
How to Pass the Pilot Licensing Exam?
Passing the pilot licensing exam is a critical step in becoming a certified pilot. It requires thorough preparation and a comprehensive understanding of aviation concepts. Here are some tips to help you succeed in the pilot licensing exam:
1. Study the Material Thoroughly
Begin by studying the relevant textbooks, manuals, and online resources. Focus on key topics such as aerodynamics, navigation, meteorology, and aviation regulations. Understanding these concepts is crucial for both the written and practical exams.
2. Attend Ground School
Ground school provides structured instruction on theoretical aspects of flying. Attend all classes, participate in discussions, and ask questions to clarify any doubts. Instructors can offer valuable insights and tips for the exam.
3. Practice with Mock Exams
Take practice exams to familiarize yourself with the format and types of questions you'll encounter. These mock exams help identify areas that need improvement and build confidence in answering questions under time constraints.
4. Review Practical Skills
For the practical exam, review and practice key flight maneuvers with your instructor. Focus on takeoffs, landings, emergency procedures, and navigation. Being well-prepared for the practical test ensures you demonstrate competence and confidence.
5. Stay Calm and Focused
On the day of the exam, stay calm and focused. Manage stress by taking deep breaths and maintaining a positive mindset. Confidence in your preparation will help you perform better during the exam.
6. Learn from Feedback
After the exam, seek feedback from your instructor or examiner. Understand any mistakes and areas for improvement. Continuous learning and practice will enhance your skills and prepare you for future challenges.
Passing the pilot licensing exam requires dedication, preparation, and a thorough understanding of aviation concepts. By following these tips and seeking guidance from experienced instructors, aspiring pilots can successfully navigate the exam process and obtain their pilot license.
Career Paths for Pilots
The aviation industry offers a wide range of career paths for pilots, each with its own set of opportunities and challenges. Here are some of the most common career paths for pilots:
1. Commercial Airline Pilot
Commercial airline pilots fly passenger aircraft for major airlines. They are responsible for transporting passengers safely and efficiently across domestic and international routes. This career path offers competitive salaries, benefits, and opportunities for career advancement.
2. Cargo Pilot
Cargo pilots transport goods and freight across various locations. They play a crucial role in the supply chain, ensuring timely delivery of essential goods. Cargo pilots may work for major logistics companies or smaller freight operators.
3. Corporate Pilot
Corporate pilots fly private jets for businesses, executives, and high-profile individuals. This role offers a varied flying experience, with pilots often traveling to unique and remote destinations. Corporate pilots enjoy flexibility and the opportunity to work closely with clients.
4. Flight Instructor
Flight instructors teach aspiring pilots how to fly. They provide ground school instruction and practical flight training, helping students achieve their pilot licenses. This career path is ideal for pilots who enjoy teaching and mentoring others.
5. Military Pilot
Military pilots operate aircraft for defense and security purposes. They undergo rigorous training and are responsible for various missions, including reconnaissance, transport, and combat. Military pilots gain invaluable experience and skills applicable to civilian aviation careers.
6. Charter Pilot
Charter pilots fly on-demand flights for individuals, groups, or businesses. They offer flexibility and personalized service, catering to clients' specific travel needs. Charter pilots may work for charter companies or operate independently.
Each career path offers unique experiences and opportunities for growth. Aspiring pilots should consider their interests, goals, and lifestyle preferences when choosing a career path. With dedication and skill development, pilots can achieve success in their chosen aviation careers.
Continuing Education for Pilots
Continuing education is essential for pilots to stay current with industry standards, regulations, and technological advancements. It ensures pilots maintain proficiency and safety in their flying skills. Here are some ways pilots can pursue continuing education:
1. Recurrent Training
Recurrent training is mandatory for pilots to refresh their skills and knowledge. It includes regular simulator sessions, classroom instruction, and practical flight training. This training ensures pilots remain competent and prepared for various scenarios.
2. Advanced Certifications and Ratings
Pilots can pursue advanced certifications and ratings to enhance their qualifications and career prospects. Options include obtaining an instrument rating, multi-engine rating, or airline transport pilot license. These certifications provide specialized skills and open new opportunities.
3. Online Courses and Seminars
Online courses and seminars offer flexible learning options for pilots to expand their knowledge. Topics range from aviation safety and regulations to emerging technologies and industry trends. These resources help pilots stay informed and engaged with the aviation community.
4. Professional Associations
Joining professional associations provides access to valuable resources, networking opportunities, and industry events. Associations such as the Aircraft Owners and Pilots Association (AOPA) and the Experimental Aircraft Association (EAA) offer workshops, publications, and conferences for pilots.
5. Specialized Training Programs
Specialized training programs focus on specific areas of interest, such as aerobatic training, mountain flying, or airshow performance. These programs enhance a pilot's skills and provide unique flying experiences.
6. Mentorship and Networking
Mentorship and networking with experienced pilots offer valuable insights and guidance. Building relationships with industry professionals provides opportunities for learning, growth, and career advancement.
Continuing education is a lifelong commitment for pilots. By actively seeking learning opportunities and staying engaged with the aviation community, pilots can maintain their proficiency and achieve long-term success in their careers.
What are the Challenges of Being a Pilot?
While a career as a pilot offers many rewards, it also comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding these challenges helps aspiring pilots prepare for and navigate the demands of the profession. Here are some common challenges pilots face:
1. Irregular Schedules
Pilots often work irregular schedules, including weekends, holidays, and overnight flights. This can lead to disruptions in personal life and challenges in maintaining a work-life balance.
2. Long Hours and Fatigue
Long hours and extended periods of alertness can lead to fatigue, which affects a pilot's performance and decision-making abilities. Managing rest and recovery is crucial for maintaining safety and well-being.
3. High Responsibility
Pilots bear significant responsibility for the safety of passengers, crew, and aircraft. This pressure requires strong decision-making skills and the ability to handle high-stress situations effectively.
4. Continuous Learning
The aviation industry is constantly evolving, requiring pilots to engage in continuous learning and training. Staying updated with new technologies, regulations, and procedures is essential for maintaining proficiency.
5. Weather and Environmental Challenges
Pilots must navigate various weather conditions and environmental challenges, such as turbulence, thunderstorms, and limited visibility. Adapting to these conditions requires skill and experience.
6. Regulatory Compliance
Pilots must adhere to strict regulatory requirements and safety protocols. Ensuring compliance with these standards is crucial for maintaining certification and operating safely.
Despite these challenges, a career as a pilot offers immense satisfaction and opportunities for growth. By understanding and preparing for these challenges, aspiring pilots can develop the resilience and skills needed to succeed in the aviation industry.
Important Regulations and Safety Protocols
Adhering to regulations and safety protocols is paramount in the aviation industry. These standards ensure the safety of pilots, passengers, and aircraft. Here are some important regulations and safety protocols pilots must follow:
1. Federal Aviation Regulations (FARs)
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) outlines regulations that govern all aspects of civil aviation in the United States. These regulations cover pilot certification, aircraft operation, airspace management, and safety standards.
2. International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) Standards
The ICAO sets international standards for aviation safety. Pilots must be familiar with ICAO regulations, especially when flying internationally, to ensure compliance with global aviation standards.
3. Air Traffic Control (ATC) Procedures
ATC provides instructions and guidance for safe and efficient aircraft movement. Pilots must adhere to ATC instructions and procedures to ensure safe navigation and avoid conflicts with other aircraft.
4. Pre-Flight Checks
Pre-flight checks are essential for ensuring the aircraft is in safe operating condition. Pilots must conduct thorough inspections of the aircraft's systems, instruments, and equipment before each flight.
5. Emergency Procedures
Pilots must be trained in emergency procedures to handle unexpected situations, such as engine failures, turbulence, or adverse weather conditions. Regular training and drills ensure pilots are prepared to respond effectively.
6. Safety Management Systems (SMS)
SMS is a systematic approach to managing safety in aviation operations. It involves identifying hazards, assessing risks, and implementing measures to mitigate safety issues. Pilots play a crucial role in maintaining and improving safety through SMS.
Understanding and adhering to these regulations and protocols is essential for pilots to ensure safe and efficient aviation operations. By prioritizing safety and compliance, pilots contribute to the overall safety and reliability of the aviation industry.
How to Maintain a Balanced Lifestyle as a Pilot?
Maintaining a balanced lifestyle is crucial for pilots to manage the demands of their profession while ensuring personal well-being. Here are some tips for pilots to achieve a healthy work-life balance:
1. Prioritize Rest and Sleep
Ensure you get adequate rest and sleep, especially before and after long flights. Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a conducive sleep environment to improve sleep quality.
2. Practice Stress Management
Engage in activities that help reduce stress, such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies. Find healthy outlets for stress relief and incorporate them into your routine.
3. Maintain a Healthy Diet
Adopt a balanced diet rich in nutrients to support overall health and energy levels. Avoid excessive caffeine and alcohol, and stay hydrated to combat fatigue.
4. Stay Connected with Family and Friends
Make time for family and friends, even with a busy flight schedule. Keep in touch through calls, messages, or video chats to maintain strong relationships.
5. Set Clear Boundaries
Establish boundaries between work and personal life. Communicate your availability to colleagues and loved ones to manage expectations and avoid burnout.
6. Pursue Personal Interests
Engage in activities and hobbies outside of flying. Pursuing personal interests provides a sense of fulfillment and helps maintain a balanced lifestyle.
By implementing these strategies, pilots can achieve a balanced lifestyle that supports their professional responsibilities and personal well-being. Prioritizing self-care and maintaining a healthy work-life balance contribute to long-term success and satisfaction in the aviation career.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the minimum age to become a pilot?
The minimum age to obtain a private pilot license is 17 years old. However, you can start flight training at a younger age with a student pilot license.
2. How long does it take to become a commercial pilot?
The time it takes to become a commercial pilot varies, but it typically ranges from 1 to 3 years, depending on the training program and the number of flight hours required.
3. Can I become a pilot if I wear glasses?
Yes, you can become a pilot if you wear glasses. As long as your vision can be corrected to meet the required standards, you can obtain a medical certification to fly.
4. What is the cost of flight training?
The cost of flight training varies depending on the location, type of license, and flight school. On average, training costs range from $5,000 to $20,000 for a private pilot license and $30,000 to $70,000 for a commercial pilot license.
5. Can I work as a pilot part-time?
Yes, some pilots work part-time, especially in roles such as flight instructors or charter pilots. Part-time opportunities offer flexibility and the chance to balance other commitments.
6. Is it difficult to find a job as a pilot?
Job prospects for pilots vary depending on the region, industry demand, and economic conditions. While the aviation industry is growing, competition can be intense, especially for entry-level positions. Gaining experience and additional certifications can enhance your job prospects.
Conclusion
Becoming a pilot is a rewarding journey that requires dedication, education, and skill development. From understanding the types of pilot licenses to choosing the right flight school, meeting medical requirements, and gaining flight experience, each step is crucial for achieving your dream of flying. By pursuing continuing education and maintaining a balanced lifestyle, pilots can ensure long-term success and satisfaction in their careers. With the right preparation and mindset, you can navigate the challenges and opportunities of the aviation industry and soar to new heights as a skilled pilot.
For further information on aviation careers and training, you can explore resources provided by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA).